Cluster Types and Concepts
Cluster types such as Management clusters, Managed clusters, and Attached clusters are key concepts in understanding and getting the most out of DKP Essential versus Enterprise environments.
Multi-cluster Environment
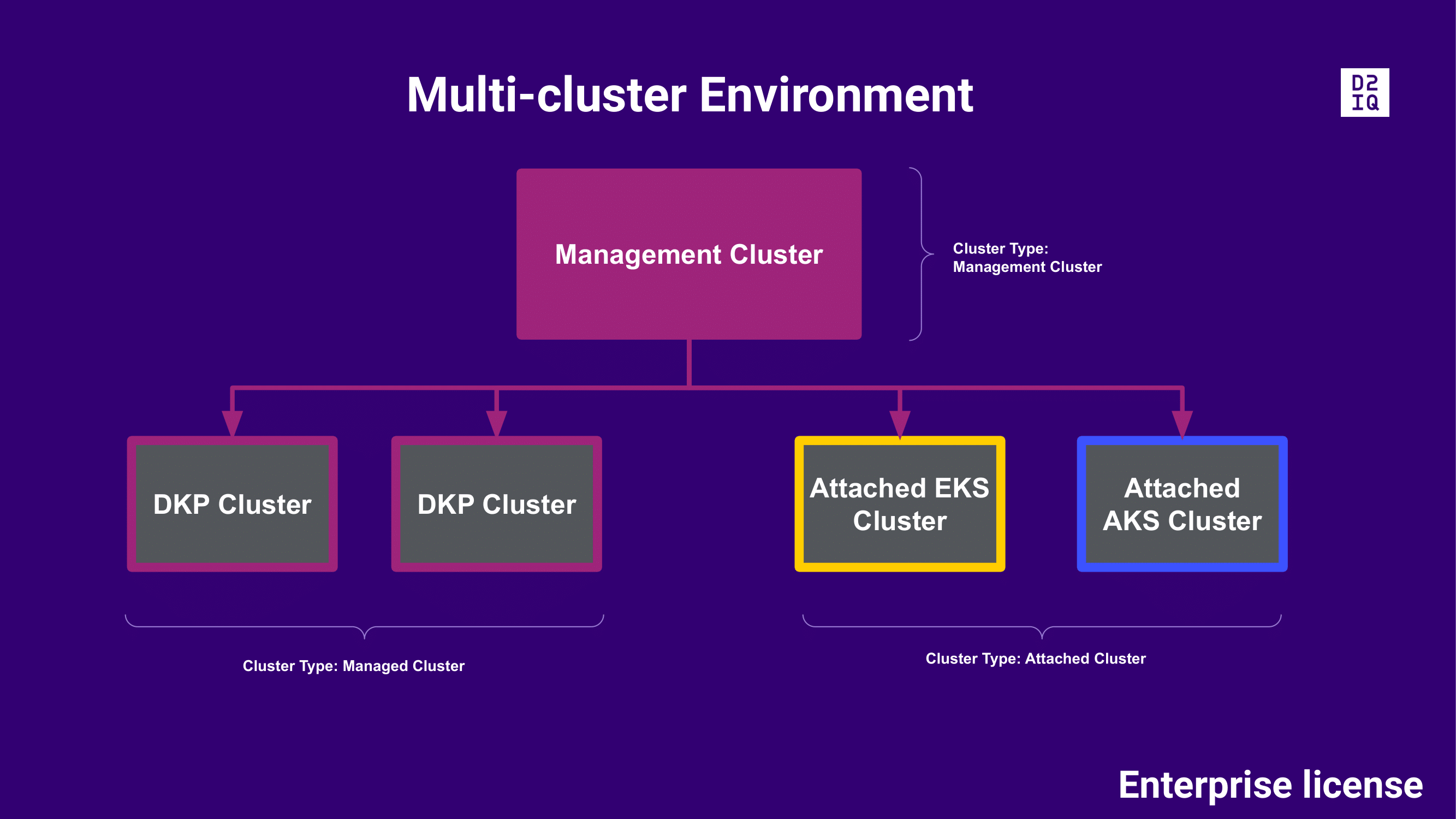
Management Cluster: Is the cluster where you install DKP, and it is self-managed. In a multi-cluster environment, the Management cluster also manages other clusters.
Customers with an Enterprise license should run workloads on Managed and Attached clusters, and not on the Management cluster.
Managed Cluster: Also called a “DKP cluster,” this is a type of workload cluster that you can create with DKP. The DKP Management cluster manages its infrastructure, its lifecycle, and its applications.
Attached Cluster: A type of workload cluster that is created outside of DKP, but is then connected to the DKP Management Cluster so that it can be managed by DKP. In these cases, the DKP Management cluster only manages the attached cluster’s applications.
Single-cluster Environment
-2-1.png?inst-v=d47a54c4-ff5d-4ef9-b867-41e26a099d62)
DKP Essential Cluster: Is the cluster where you install DKP. A DKP Essential cluster is a stand-alone cluster. It is self-managed and therefore capable of provisioning itself. In this single-cluster environment, you cannot attach other clusters and all workloads are run on your DKP Essential cluster. You can, however, have several separate DKP Essential instances, each with its own license.
Customers with an Essential license can run workloads on their DKP Essential cluster.
If you have not decided which license to get, but plan on adding one or several clusters to your environment, and manage them centrally, D2iQ recommends obtaining an Enterprise license.
Other important concepts
Self-managed Cluster: In a DKP landscape, only DKP Essential and DKP Enterprise Management clusters are self-managed. Self-managed clusters are clusters that manage the provisioning, and deployment of its own nodes through CAPI controllers. The CAPI controllers are a managing entity, which automatically manages the lifecycle of a cluster’s nodes based on a customizable definition of the resources.
A self-managed cluster refers to one in which the CAPI resources and controllers that describe and manage it are running on the same cluster they are managing. As part of the underlying processing using the --self-managed flag, the DKP CLI:
creates a bootstrap cluster
creates a workload cluster
moves CAPI controllers from the bootstrap cluster to the workload cluster, making it self-managed
deletes the bootstrap cluster
Network-Restricted Cluster:
(NOT equivalent to air-gapped)
A network-restricted or firewalled cluster is secured by a firewall, DMZ, NAT gateway, proxy server, or requires additional access information. Network-restricted clusters are usually located in remote locations or at edge, and therefore not in the same network as the Management cluster.
The main difference between network-restricted and air-gapped clusters is that network-restricted clusters can reach external networks (like the Internet), but its services or ingresses cannot be accessed from outside. Air-gapped clusters, on the other hand, do not allow ingress, nor egress traffic.
In a multi-cluster environment, DKP supports attaching a network-restricted cluster to a DKP Management cluster. You can also enable a proxied access pipeline through the Management cluster, which allows you to access the network-restricted cluster’s dashboards without being in the same network.
.png)